Is 3D Printing The Future Of The Space Industry?
Within the last few years, a lot has changed in the space industry. One of the biggest differences is how companies are building rockets. However, companies such as SpaceX are not the only ones starting to do it differently. Smaller businesses like Rocket lab and Relativity Space are working on rockets and engines built with a 3D printer.
In the future, 3D printing will likely become one of the more popular ways to create rockets. While it won’t replace a lot of the current building processes, it will definitely expand. This is because of the benefits 3D printing provides including lower costs, faster production, and better reliability. Each reason is pushing more companies to work with and try 3D printing in the space industry.
Companies are always looking for innovative and unique solutions to different problems. One consistent problem when building rockets is the amount of money needed and how long it takes to produce them. This not only is the case when building the main rocket stage but also engines and other parts. Currently, 3D printing in the space industry is expanding rapidly and being used in a lot of different scenarios.
What Private Space Companies Are Using 3D Printing?

Two of the main private space companies that are 3D printing rockets or engines are Relativity Space and Rocket Lab. Starting with Rocket Lab they are a private company who for the most part has been working on their small lift launch vehicle. This rocket is named Electron and stands at 18m tall. It has two stages, is meant to be partially reusable, and has 10 engines in total. While the rocket itself is not 3D printed the engines are. Rocket Lab’s engine is called the Rutherford rocket engine. This engine is almost entirely 3D printed. This includes the 9 engines on the first stage and the single vacuum optimized engine on the second stage. The engine is 3D printed but works just as well if not better than any other engine. It is quite small at 35kg but still manages to produce a lot of thrust.
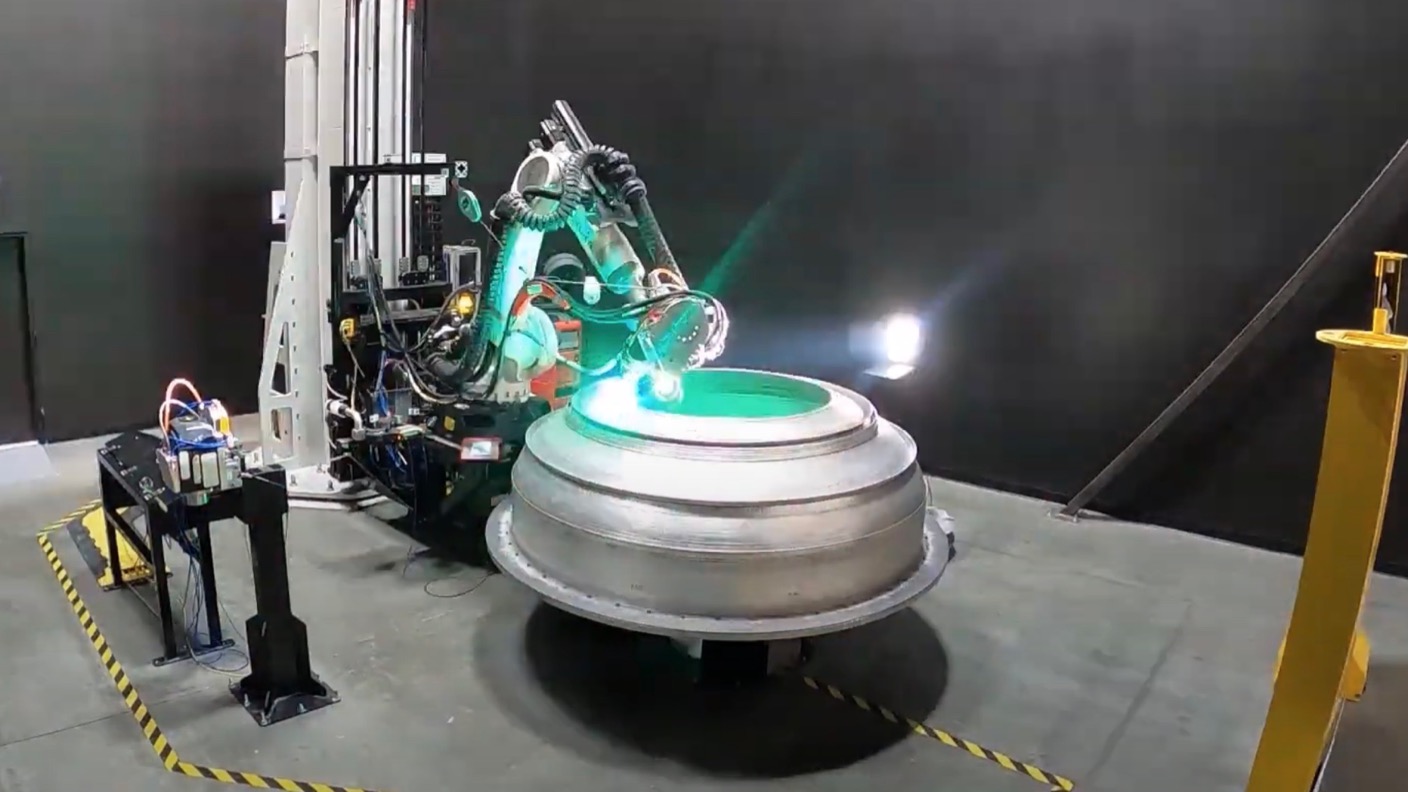
The next company I want to talk about is Relativity Space. This company is working on using an almost entirely 3D-printed rocket. Rather than just the engine or a few different parts, they are printing the entire rocket. I am going to focus on the main rocket stages and the engines. Relativity has multiple rockets they are currently developing and working on. This includes Terran 1 and Terran R which are both planned to be 3D-printed rockets. Terran 1 is the smaller of the two and is farther in development. Using the largest metal 3D printers Relativity is able to print massive sections of the rocket. The company also prints its engines as well. They have multiple engines including the Aeon 1, Aeon R and Aeon Vac, which are all 3D-printed. Relativity is early in development but they are making great progress towards their ambitious goals.
How Does 3D Printing A Rocket Work?
When printing a rocket it all starts with the 3D printer itself. Relativity for example uses a very large metal 3D printer. Here the printer is set up with a large roll of metal alloy. The company picks whatever material they want the rocket to be made of. Once the printer has its necessary material it is turned on and starts to print. The machine goes in a large circle and melts the metal into place. They heat up the material just above the melting point using an electric discharge and other methods. The printer will then continue to go in circles adding a bit of material every pass. Over time you end up with a large section of a rocket that is completely 3D printed. The process for printing an engine is a bit different, however. Rather than print one large piece, a lot of smaller pieces are printed separately. Once they are all complete they will be assembled into one working rocket engine.
Benefits Of 3D Printing
Cost – Everything related to the space industry is very expensive. This includes the process of creating and assembling a rocket no matter what the size. These high prices are often a limiting factor for a lot of different companies and agencies. This is exactly why everyone in the space industry is innovating and trying to work out ways to lower costs. One of the ways to do this is by 3D printing the rocket and its engines. A lot of different aspects have an effect on the cost of building a rocket.
Some of the main parts are labor, material, the time it takes, and more. 3D printing helps with each of these different factors. Material is a good example of the benefit of 3D printing. As I mentioned before companies like Relativity use a large printer with a roll of whatever material they need to print rockets. This material can save them a lot of money over time. The same goes for other aspects like the time it takes. With the production speed significantly faster, less money is spent on the construction process. The printer also builds the rocket basically by itself which also saves money.
Production Speed – The speed at which a company can build and launch rockets is very important. Whatever the goals of the company are, a faster production speed will significantly help the business. Rocket production time has always been a very slow process. Looking at different companies and agencies around the world you will see a similar pattern. 3D printing provides a unique solution to the problem. 3D printers are very fast and can work 24/7. This combined with their consistency means they can produce extremely complex equipment and parts such as rockets or engines in a very short period of time.
Reliability – One of the final benefits that I want to mention is reliability. While a lot of 3D printers used for rockets today are quite new, they are constantly improving. As they get better and better they will also become more consistent. Rockets are extremely complex and a lot can go wrong. With a high-quality 3D printer responsible for making them it can help improve the consistency by a long shot. This would improve the rocket’s launch record and heighten the confidence in the company and the rocket.
What Does The Future Of 3D Printing Rockets Look Like?

3D printing will not fully replace current and future ways of developing rockets but it will likely expand significantly. 3D printing provides a great opportunity for different companies to lower costs, speed up production, etc. As companies like Relativity and Rocket Lab have more success over time it will encourage more companies to try their methods. In addition, if another rocket producer wants to compete with their lower launch costs and production time they will need to innovate as well. 3D printing is in its very early stages right now in the rocket industry. It will likely expand and become a much more popular strategy in the future.
Conclusion
3D printing rockets has a lot of different benefits. This is the exact reason it will likely become a lot more popular in the future. The 3D printing process helps lower costs, speed up production, and improve the overall reliability and consistency of a rocket. Companies like Relativity and Rocket Lab are leading the way in this new technology. Both of these companies have very ambitious goals for the future of rocket development and 3D printing. As time goes on will have to see how well these rockets perform and how it impacts the space industry in the future.
